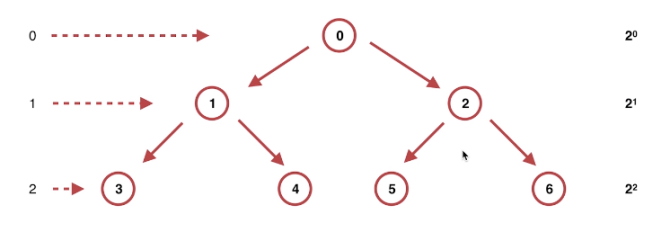
特性
一个节点只有两个子节点,左节点和右节点
实现二叉树结构
// 二叉树的节点
class Node {
constructor(val) {
this.val = val
this.left = this.right = undefined
}
}
class Tree {
constructor(data) {
// 临时存储所有节点,方便寻找父子节点
let nodeList = []
// 顶节点
let root
for (let i = 0, len = data.length; i < len; i++) {
let node = new Node(data[i])
nodeList.push(node)
if (i > 0) {
// 计算当前节点属于哪一层
let n = Math.floor(Math.sqrt(i + 1))
// 记录当前层的起始点
let q = Math.pow(2, n) - 1
// 记录上一层的起始点
p = Math.pow(2, n - 1) - 1
// 找到当前节点的父节点
let parent = nodeList[p + Math.floor((i - q) / 2)]
// 将当前节点和上一层的父节点做关联
if (parent.left) {
parent.right = node
} else {
parent.left = node
}
}
}
root = nodeList.shift()
// 释放数组
nodeList.length = 0
return root
}
}
export default Tree
export {
Node
}
对称二叉树
给定一个二叉树,检查它是否是镜像对称的。
// 例如,二叉树 [1,2,2,3,4,4,3] 是对称的。
1
/ \
2 2
/ \ / \
3 4 4 3
// 但是下面这个 [1,2,2,null,3,null,3] 则不是镜像对称的:
1
/ \
2 2
\ \
3 3
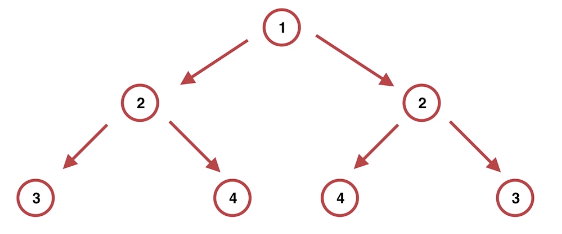
左定点的左节点等于右定点的右节点,以此类推
// 二叉树的节点
class Node {
constructor(val) {
this.val = val
this.left = this.right = undefined
}
}
class Tree {
constructor(data) {
// 临时存储所有节点,方便寻找父子节点
let nodeList = []
// 顶节点
let root
for (let i = 0, len = data.length; i < len; i++) {
let node = new Node(data[i])
nodeList.push(node)
if (i > 0) {
// 计算当前节点属于哪一层
let n = Math.floor(Math.sqrt(i + 1))
// 记录当前层的起始点
let q = Math.pow(2, n) - 1
// 记录上一层的起始点
p = Math.pow(2, n - 1) - 1
// 找到当前节点的父节点
let parent = nodeList[p + Math.floor((i - q) / 2)]
// 将当前节点和上一层的父节点做关联
if (parent.left) {
parent.right = node
} else {
parent.left = node
}
}
}
root = nodeList.shift()
// 释放数组
nodeList.length = 0
return root
}
static isSymmetry(root) {
if (!root) {
return true
}
let walk = (left, right) => {
if (!left && !right) {
return true
}
if ((left && !right) || (!left && right) || (left.val !== right.val)) {
return false
}
return walk(left.left, right.right) && walk(left.right, right.left)
}
return walk(root.left, root.right)
}
}
export default Tree
export {
Node
}
let root =new Tree([1,2,2,3,4,4,3])
console.log(Tree.isSymmetry(root))
验证二叉搜索树
给定一个二叉树,判断其是否是一个有效的二叉搜索树。
假设一个二叉搜索树具有如下特征:
- 节点的左子树只包含小于当前节点的数。
节点的右子树只包含大于当前节点的数。
所有左子树和右子树自身必须也是二叉搜索树。
// 示例 1:
输入:
2
/ \
1 3
输出: true
// 示例 2:
输入:
5
/ \
1 4
/ \
3 6
输出: false
解释: 输入为: [5,1,4,null,null,3,6]。
根节点的值为 5 ,但是其右子节点值为 4 。
所有的子树跳出来,看看是不是左边小右边大。如果所有都满足,那整个树都满足了
// 二叉树的节点
class Node {
constructor(val) {
this.val = val
this.left = this.right = undefined
}
}
class Tree {
constructor(data) {
let root = new Node(data.shift())
// 遍历所有的数据,逐渐插入到当前这课搜索树中去
data.forEach(item => {
this.insert(root, item)
})
return root
}
insert(node, data) {
if (node.val > data) {
if (node.left === undefined) {
node.left = new Node(data)
} else {
this.insert(node.left, data)
}
} else {
if (node.right === undefined) {
node.right = new Node(data)
} else {
this.insert(node.right, data)
}
}
}
static walk(root) {
if (!root.left && !root.right) {
return true
} else if (((root.left && root.val < root.left.val) || (root.right && root.val > root.right.val))) {
return false
} else {
return Tree.walk(root.left) && Tree.walk(root.right)
}
}
}
export default Tree
export {
Node
}
二叉搜索树对于排序有很大参考。
做好了排序后,插入和删除非常好操作。